Interdisciplinary Research
CSU’s Interdisciplinary Research Infrastructure
Caraga State University (CSU) has established a robust interdisciplinary research infrastructure that supports innovation, collaboration, and technology commercialization. This infrastructure is designed to enhance research capabilities, human capital development, policy frameworks, product innovation, and technology transfer mechanisms, ensuring that CSU remains a leader in transdisciplinary research and socio-economic development.
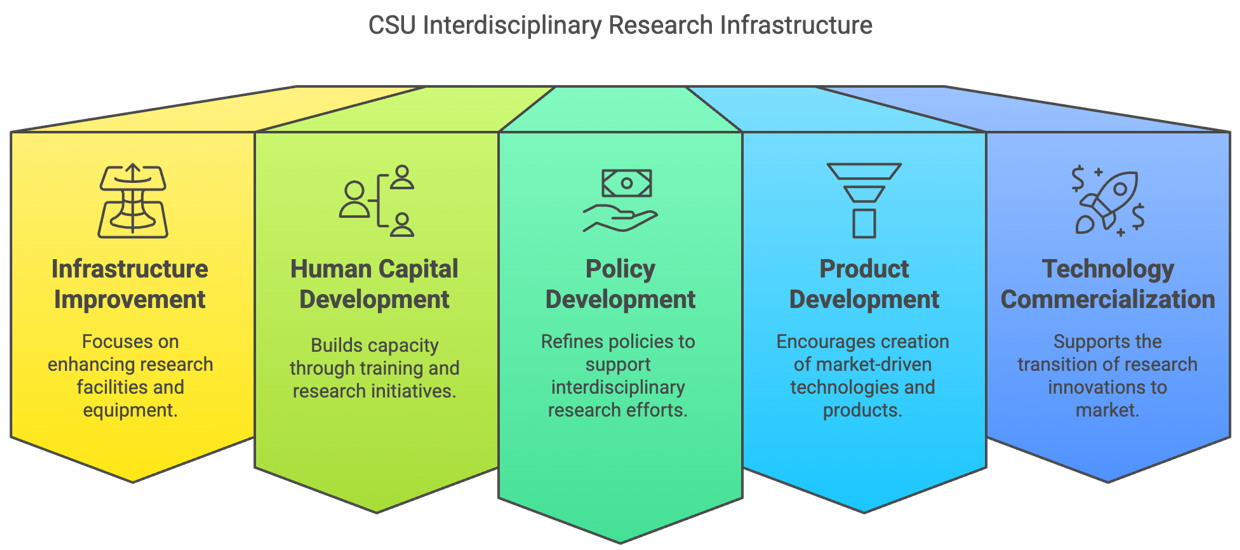
A critical pillar of this infrastructure is Infrastructure and Facilities Improvement, which involves continuous investment in research laboratories, smart research spaces, and specialized facilities. CSU has prioritized the development of state-of-the-art equipment, digital research platforms, and collaborative workspaces that enable researchers from various disciplines to work together seamlessly. These improvements ensure that faculty, students, and industry partners have access to cutting-edge tools that support scientific discovery, experimental research, and technology development.
Another key component is Human Capital Development, which focuses on building the capacity of CSU’s researchers, faculty members, and students to engage in high-impact interdisciplinary research. Through training workshops, faculty research grants, postgraduate scholarships, and international research collaborations, the university fosters an environment where researchers can develop new skills, explore emerging technologies, and collaborate with experts from different fields. By investing in faculty development programs and student research initiatives, CSU strengthens its research ecosystem and cultivates a new generation of interdisciplinary scientists and innovators.
Policy Development also plays a crucial role in CSU’s interdisciplinary research infrastructure. The university continuously refines its institutional policies to support interdisciplinary research by streamlining funding mechanisms, establishing research ethics guidelines, and creating incentive structures for cross-disciplinary collaboration. These policies help researchers secure external grants, publish in high-impact journals, and establish strong partnerships with industry and government stakeholders. By aligning research policies with national and regional development plans, CSU ensures that its interdisciplinary research contributes to economic growth, sustainability, and innovation-driven progress.
In addition to research policies, CSU places a strong emphasis on Product Development, encouraging interdisciplinary research teams to develop market-driven technologies, patents, and innovative products. The university supports researchers in transforming their ideas into commercialize solutions that address real-world challenges in areas such as renewable energy, smart technologies, agriculture, digital transformation, and healthcare. By integrating research with entrepreneurial initiatives, CSU fosters an innovation-driven culture that accelerates the translation of academic research into practical applications.
To support technology commercialization, CSU has established a Technology Transfer and Licensing Office (TTLO) and Technology Business Incubation (TBI) hubs, such as Navigatu and TARA. These incubation centers provide researchers and startups with mentorship, funding opportunities, intellectual property (IP) management services, and industry linkages, ensuring that their research innovations reach the market. The TTLO facilitates patent applications, licensing agreements, and startup development, helping CSU researchers navigate the complex process of commercializing university-generated technologies.
Through this well-structured interdisciplinary research infrastructure, CSU ensures that its research ecosystem remains globally competitive, innovation-driven, and aligned with national and international priorities. By integrating state-of-the-art facilities, human capital development, strong research policies, product innovation strategies, and technology transfer mechanisms, CSU creates an environment where interdisciplinary collaboration thrives. This commitment positions the university as a hub for scientific discovery, economic transformation, and sustainable development in the Caraga region and beyond.
The Research, Development, and Innovation (RDI) Centers
Caraga State University (CSU) has taken significant steps to provide specific physical facilities for interdisciplinary research teams within applicable disciplines. One of its major initiatives is the full operationalization of the university’s 24 Research, Development, and Innovation (RDI) Centers, which serve as collaborative hubs for interdisciplinary research. These centers are strategically designed to facilitate research in key areas such as renewable energy, artificial intelligence, sustainable agriculture, health and nutrition, environmental conservation, and emerging technologies. Each RDI Center is equipped with specialized laboratories, advanced research equipment, and digital platforms to support cutting-edge scientific studies.
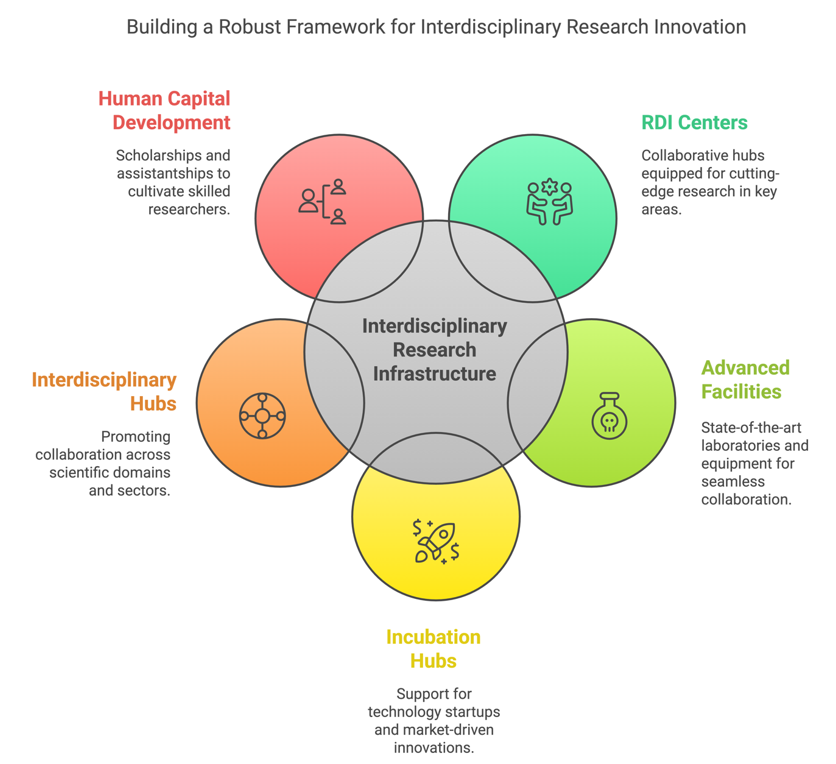
Additionally, CSU is continuously upgrading its laboratory facilities and research infrastructure to accommodate the growing demand for interdisciplinary research. The university has invested in state-of-the-art equipment, smart laboratories, and digital research platforms that enable researchers from different disciplines to collaborate seamlessly. These facilities not only enhance the research capacity of faculty and students but also strengthen industry linkages by fostering university-industry collaborations that bridge the gap between academic research and practical applications.
CSU also provides incubation facilities for technology startups and commercialization initiatives through its Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) such as Navigatu and TARA. These incubation hubs support researchers, entrepreneurs, and interdisciplinary teams in developing market-driven innovations. Furthermore, the university’s Technology Transfer and Licensing Office (TTLO) plays a crucial role in facilitating intellectual property (IP) management, technology transfer, and commercialization efforts.
Moreover, CSU has established interdisciplinary research hubs that promote collaboration across various scientific domains. These hubs are designed to encourage cross-sectoral partnerships and knowledge-sharing among researchers, industry stakeholders, and government agencies. The university also provides scholarships and research assistantships to cultivate a pipeline of highly skilled graduate researchers who contribute to interdisciplinary projects.
Through these initiatives, CSU ensures that its research infrastructure supports interdisciplinary collaboration, fosters technological innovation, and enhances the university’s global research competitiveness. The continuous investment in research facilities and human capital development underscores CSU’s commitment to becoming a leading institution for transdisciplinary research, innovation, and sustainable development.
Caraga State University’s Research, Development, and Innovation Centers
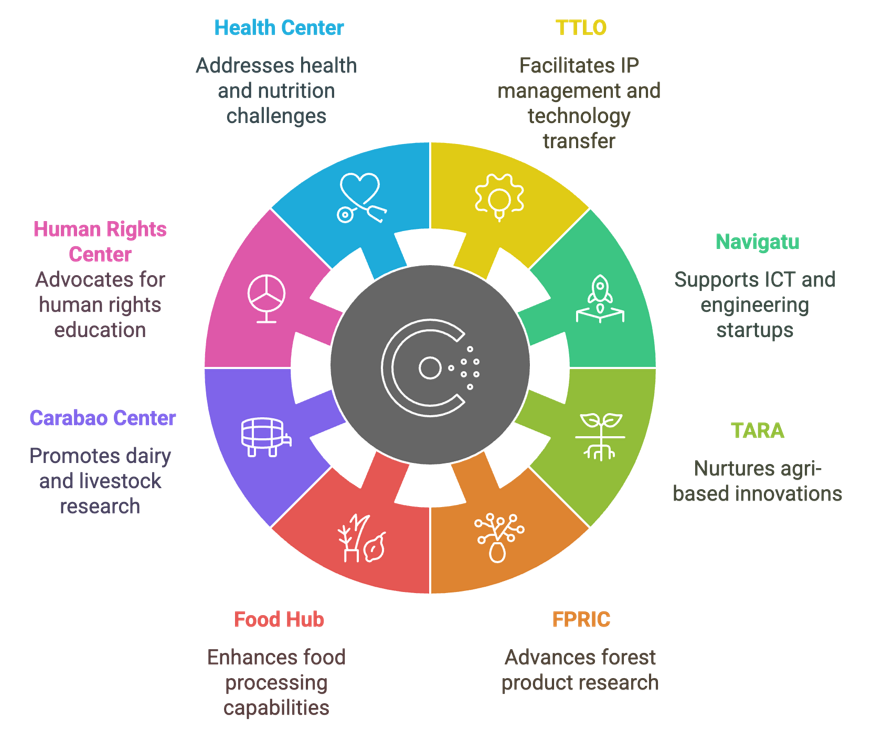
There are 24 RDI Centers at Caraga State University including the Innovation and other upcoming research centers: Technology Transfer and Licensing Office (TTLO), Food Innovation Centers (FICs), and Technology Business Incubation (TBI) Hubs.
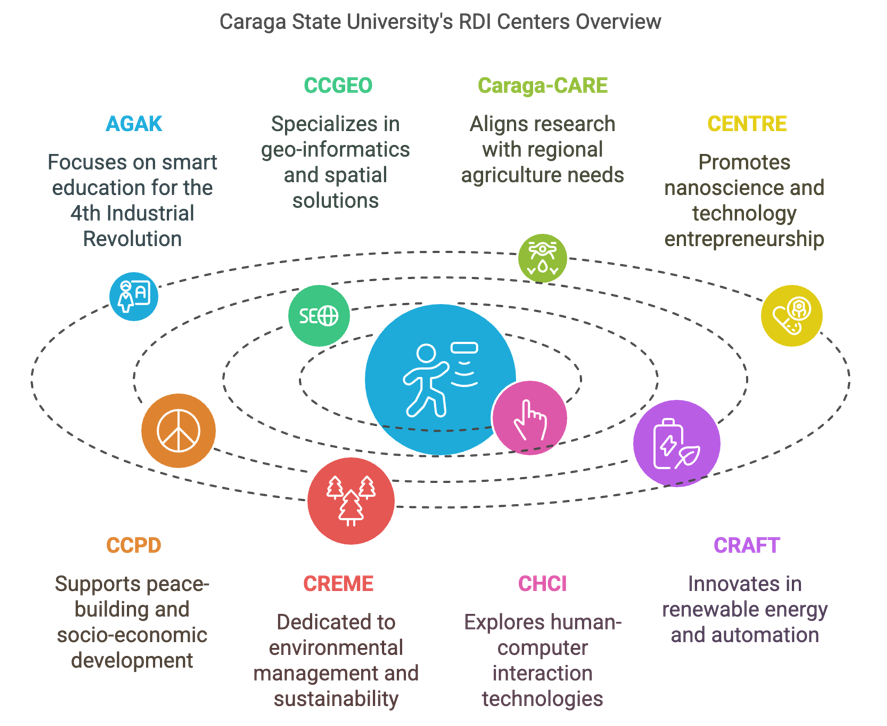
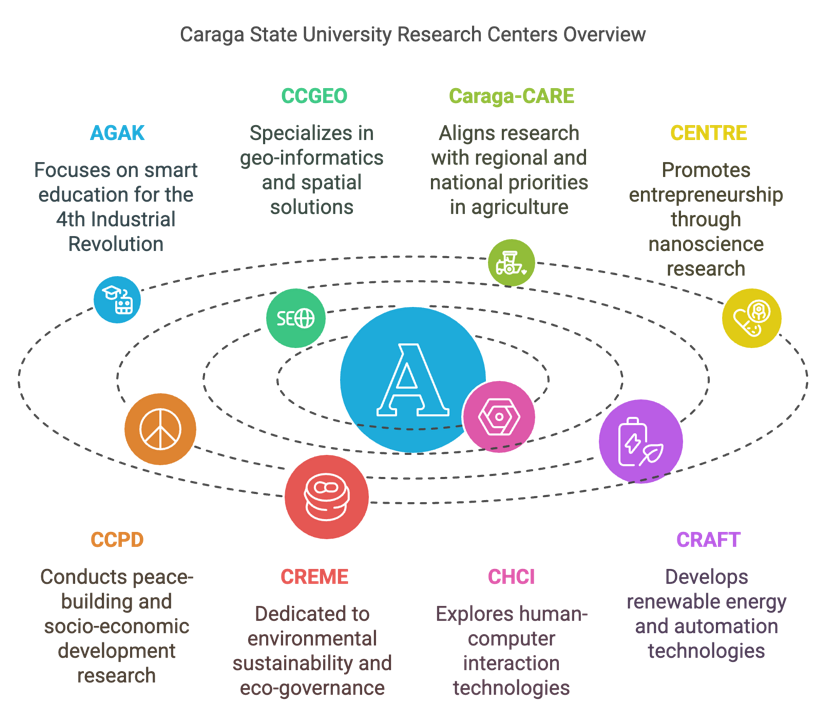
1. AGAK (Advancing Growth and Knowledge)
The AGAK Center leads research and development programs aimed at preparing Caraga for the 4th Industrial Revolution. It focuses on smart education and applying innovative pedagogies to help learners master 21st-century skills and knowledge, ensuring the region remains competitive in a rapidly evolving global landscape.
2. CCGEO (Caraga Center for Geo-Informatics)
The CCGEO Center specializes in geo-informatics, conducting interdisciplinary research and extension activities in Surveying, Geodesy, and Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS). Its work supports spatial solutions and development initiatives, strengthening the region’s capacity for data-driven decision-making.
3. Caraga-CARE
The Caraga-CARE Center aligns its research with regional and national priorities, focusing on thematic areas that leverage the strengths of faculty researchers in Agriculture and Agro-Industries. Its mission is to address local challenges while contributing to broader societal impact through innovative research.
4. CENTRE (Center for Nanoscience and Technology for Research and Entrepreneurship)
Established in 2019, CENTRE focuses on advanced research in nanoscience and promotes entrepreneurship by developing technologies with practical applications. It fosters innovation to address pressing scientific and industrial needs.
5. CCPD (Caraga Center for Peace and Development)
The CCPD Center promotes active citizenship, socio-economic development, and peace-building. It conducts research and capacity-building programs to achieve inclusive and sustainable growth while fostering regional stability and development.
6. CREME (Center for Research on Environmental Management and Eco-Governance)
CREME is dedicated to ensuring environmental sustainability through eco-governance research. It focuses on managing land, air, and water resources effectively, contributing to sustainable development practices in the region.



7. CHCI (Center for Human and Computer Interaction)
The CHCI Center explores the foundations of human-computer interaction technology, focusing on its applications in learning, environmental, and rural contexts. Its work aims to enhance user-centered technologies that improve community engagement.





8. CRAFT (Center for Renewable Energy, Automation, and Fabrication Technology)
The CRAFT Center promotes research in renewable energy, automation, and applied multidisciplinary technologies. It aims to develop innovative solutions that address energy and automation challenges in the region.



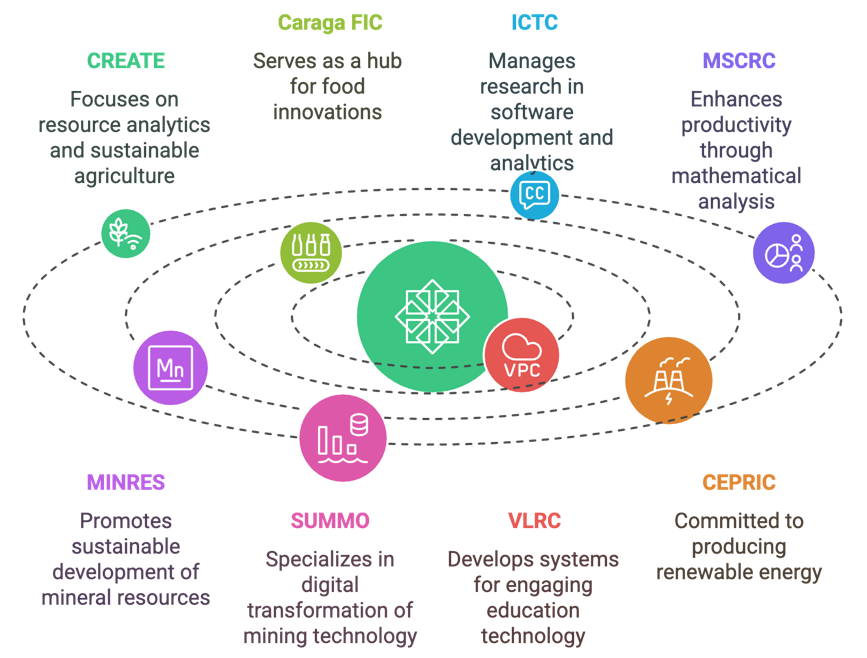
9. CREATE (Center for Resource Analytics and Emerging Technologies)
CREATE focuses on resource analytics and agricultural landscapes, utilizing Caraga Region’s resources as platforms for research and innovation. Its work supports sustainable practices and agricultural advancement.



10. Caraga FIC (Caraga Food Innovation Center)
The Caraga FIC Center serves as a hub for food innovations, providing value-adding services and technical support to enhance the development of processed foods. It drives innovation in the regional food industry.


11. ICTC (Information and Communication Technology Center)
The ICTC Center manages research in software development, predictive analytics, and project management, offering technological solutions such as software as a service to support Caraga’s ICT initiatives.



12. MSCRC (Mathematical and Statistical Computing Research Center)
MSCRC enhances productivity through mathematical and statistical analysis, conducting research with integrity and reliability to support evidence-based solutions in various fields.


13. MINRES (Mindanao Institute for Mineral Resources Management Research and Training)
MINRES integrates various disciplines to promote the sustainable development of mineral resources in the region. Its science-based research supports responsible mining and resource management.
14. SUMMO (Smart Urban Mining and Monitoring Operations)
The SUMMO Center focuses on the digital transformation of mining technology, specializing in tools like IoT, AI, and data analytics for monitoring and evaluation, enhancing mining sustainability and efficiency.
15. VLRC (Virtual Learning Research Center)
The VLRC Center develops systems and applications using AI and software frameworks to make teaching and learning more engaging. It fosters innovation in education technology.


16. CEPRIC (Clean Energy and Power Research and Innovation Center)
CEPRIC is committed to enhancing energy efficiency by producing clean, dependable, and renewable energy for Caraga, even in remote areas, contributing to the region’s long-term energy sustainability.
17. TTLO (Technology Transfer and Licensing Office)
The TTLO serves as the primary hub for intellectual property (IP) management, technology transfer, and licensing at Caraga State University. It facilitates the commercialization of research outputs, providing guidance on patent applications, licensing agreements, and industry collaboration to ensure that CSU’s innovations reach the market and benefit society.





18. Navigatu (Technology Business Incubator) for ICT and Engineering
Navigatu is one of CSU’s Technology Business Incubators (TBIs), designed to support startups and entrepreneurial ventures in the region. It provides mentorship, networking opportunities, and access to resources that enable innovative ideas to evolve into sustainable businesses, focusing on technology-driven solutions.




19. TARA (Technology Business Hub) for Agri-based Innovations
TARA is another Technology Business Hub at CSU, fostering innovation and entrepreneurship in the agriculture. It focuses on nurturing early-stage startups, providing incubation services such as prototyping support, market validation, and business model development, particularly in agri-tech, renewable energy, and digital innovation.


20. Caraga FPRIC (Forest Products Research Innovation Center)
The Caraga Forest Products Research & Development, Innovation Center (FPRIC) at CSU is dedicated to advancing research on forest-based products and sustainable forestry practices. It emphasizes value-added innovations in wood, non-timber forest products, and biomaterials to support the sustainable management of forest resources while fostering economic growth in the region.

21. CSU Cabadbaran Food Innovation Hub
The CSU Cabadbaran Food Innovation Hub focuses on enhancing the region’s food processing capabilities by providing innovative solutions, technical support, and training to food producers and entrepreneurs.
22. The Philippine Carabao Center at CSU
The Carabao Center at Caraga State University is dedicated to advancing research and development in dairy production, carabao-based products, and livestock management. It focuses on promoting sustainable agricultural practices by improving milk production, processing technologies, and value-added dairy products, such as yogurt, cheese, and other derivatives.
23. CSU Center for Human Rights and Education
The CSU Center for Human Rights and Education is committed to promoting human rights awareness, advocacy, and education within the Caraga Region. Established in 2024 in cooperation with the Commission on Human Rights (CHR), it serves as a platform for research, capacity-building, and community engagement on issues related to human dignity, equality, and social justice.
24. Center for Health and Nutrition Research (upcoming for School of Medicine)
The Center for Health and Nutrition Research is dedicated to addressing health and nutrition challenges in the Caraga Region through evidence-based research and innovative solutions. The center focuses on public health initiatives, nutrition studies, and interventions aimed at improving the overall well-being of communities, especially vulnerable populations. Key areas of research include malnutrition prevention, food fortification, maternal and child health, and the development of community-based health programs. The center also collaborates with local government units, healthcare providers, and international organizations to design sustainable policies and programs that enhance healthcare delivery and nutritional outcomes. Aligned with Caraga State University’s commitment to fostering healthy and resilient communities, the center contributes to achieving regional and national goals in health equity and food security.
Strategic Importance of CSU’s RDI Centers
The establishment of RDI Centers at CSU represents a strategic investment in knowledge creation, technology transfer, and industry-academe collaboration:
- Enhance Research Capacity: Facilitate cutting-edge research in priority areas such as renewable energy and emerging technologies, health and nutrition, sustainable agriculture, AI-driven solutions, and environmental conservation.
- Strengthen Industry Linkages: Foster university-industry collaborations to bridge the gap between academic research and market-driven innovations.
- Support Startups and Technology Commercialization: Provide incubation facilities for tech startups, support intellectual property (IP) generation, and promote spinoff ventures.
- Promote Regional Competitiveness: Develop data-driven policy solutions, digital transformation strategies, and knowledge-based innovations to enhance Caraga’s economic growth.
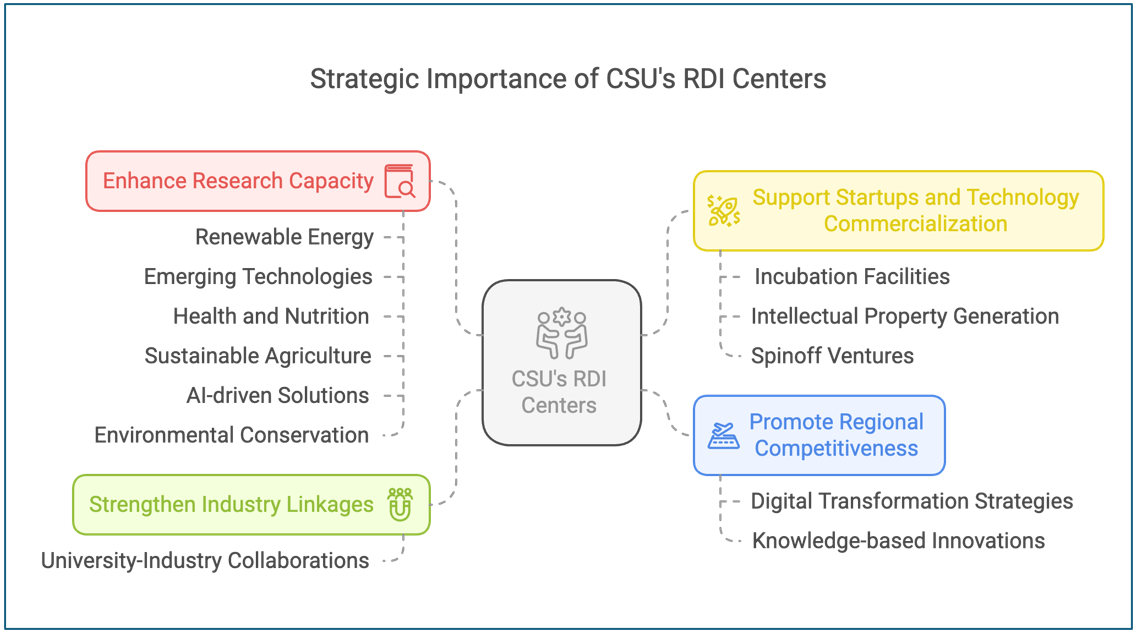
The operationalization of these RDI Centers positions Caraga State University as a leader in interdisciplinary research-driven regional development, making science, technology, and innovation the backbone of Caraga’s transformation. By ensuring alignment with the PDP and RDP, this initiative reinforces CSU’s role in shaping a resilient, inclusive, and innovation-driven future for the region and the nation.
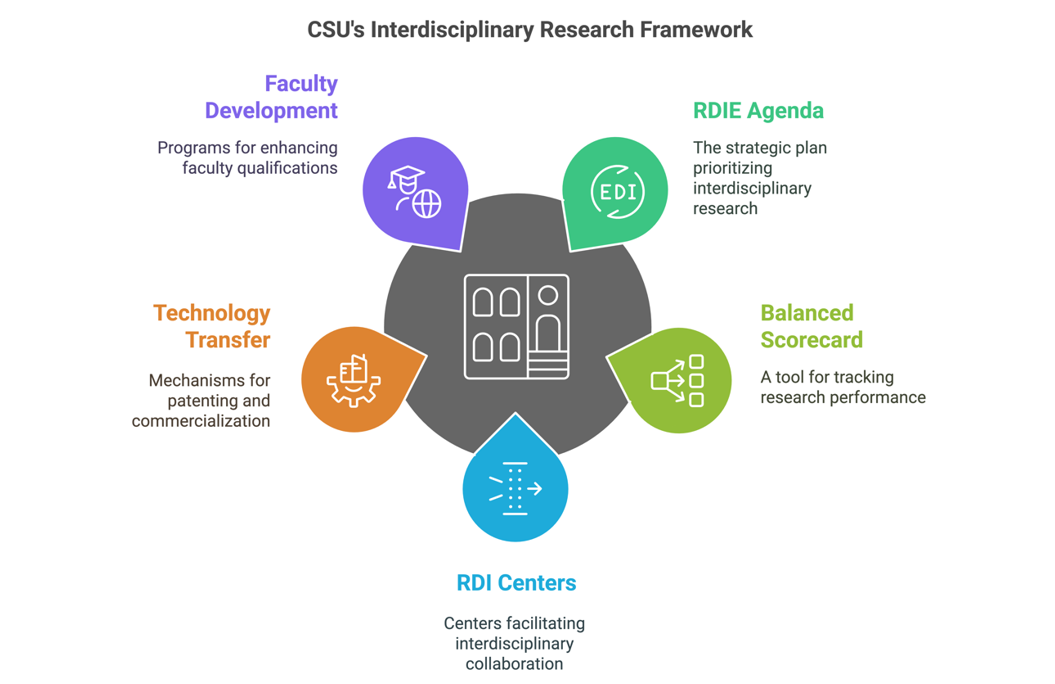
CSU Administration’s Support in Interdisciplinary Research
Caraga State University (CSU) provides comprehensive administrative support to interdisciplinary research teams, ensuring that faculty, researchers, and students have the necessary resources and institutional backing to engage in high-impact, multi-sectoral research. This administrative support is embedded within CSU’s Research, Development, Innovation, and Extension (RDIE) Agenda 2026-2030, which prioritizes strategic research initiatives, funding opportunities, research governance, and capacity-building programs for faculty and students.
The Research, Development, and Innovation (RDI) Centers
One of the key mechanisms of administrative support at CSU is the full operationalization of its 24 Research, Development, and Innovation (RDI) Centers, which serve as institutional hubs for interdisciplinary collaboration. These centers are structured to facilitate research in renewable energy, artificial intelligence, health and nutrition, sustainable agriculture, digital transformation, and environmental conservation, among others. Each center is equipped with administrative and technical support to assist researchers in conducting interdisciplinary studies, managing projects, and securing external funding.
CSU also provides structured research funding support through various grants and scholarships aimed at encouraging faculty and student participation in interdisciplinary research. The university administers research incentives and seed funding to support early-stage research projects, technology commercialization, and start-up incubation. These funding mechanisms are designed to ensure that interdisciplinary teams have financial stability and institutional support to develop innovative solutions with real-world applications.
To further strengthen interdisciplinary research, CSU has established Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) such as Navigatu and TARA, which provide funding, mentorship, and industry linkage opportunities for researchers aiming to commercialize their innovations. The Technology Transfer and Licensing Office (TTLO) plays a crucial role in intellectual property (IP) management, patent filing, and technology licensing, ensuring that interdisciplinary research outputs are protected and successfully transferred to industry and society.
Funding
Caraga State University, through the General Appropriations Act (GAA) provides research funding for CSU researchers annually in interdisciplinary research. The present funding at Php 7.6 Million (USD 132,449.18) shall be increased to Php 59 Million (USD 1,028,223.87) in 2026-2030.
Also in 2023, there were a total of Php 39,000,000.00 (USD 679,673.41) worth of funding from GAA that were provided to do interdisciplinary research from GAA.
Research Governance
In terms of research governance, CSU implements a Balanced Scorecard approach to track research performance, innovation progress, and institutional development. This structured monitoring system enables administrators to assess the impact of interdisciplinary research projects, ensuring efficient resource allocation and alignment with national and regional priorities. Additionally, faculty participation in research and extension activities is actively monitored to encourage higher engagement in interdisciplinary research, international collaborations, and industry partnerships.
Interdisciplinary Research and Innovation Centers

Tenure or Career Promotion System in Interdisciplinary Research
Caraga State University (CSU) has established a tenure and career promotion system that recognizes interdisciplinary research within applicable disciplines. This system aligns with the university’s Research, Development, Innovation, and Extension (RDIE) Agenda 2026-2030, which prioritizes interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary research as a key driver of academic excellence, technological innovation, and societal impact.
One of the primary mechanisms through which CSU acknowledges interdisciplinary research in tenure and career progression is its Balanced Scorecard approach for tracking research performance. This approach ensures that faculty participation in interdisciplinary research projects, industry collaborations, and international research partnerships are actively monitored and credited toward career advancement. The system evaluates faculty research contributions based on the number of indexed publications (Scopus, Web of Science), citations, external funding secured, and research outputs that lead to policy contributions or technology commercialization.
Additionally, CSU’s tenure and promotion system rewards faculty engagement in collaborative, multi-disciplinary research initiatives conducted through the university’s 24 Research, Development, and Innovation (RDI) Centers. These centers facilitate interdisciplinary collaboration across fields such as renewable energy, artificial intelligence, food security, sustainable agriculture, geoinformatics, health and nutrition, and digital transformation. Faculty members who actively contribute to these centers and produce high-impact research are eligible for accelerated promotions and research incentives.
Moreover, CSU integrates technology transfer and commercialization impact into its tenure evaluation criteria. Faculty members who successfully file patents, develop intellectual property, secure licensing agreements, or launch start-up ventures based on interdisciplinary research receive additional career progression points as per the Department of Budget and Management (DBM) Joint Circular No. 3, s. 2022, or otherwise known as the JC3 in the Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
The Technology Transfer and Licensing Office (TTLO) plays a key role in assisting faculty with intellectual property management and ensuring that research innovations reach the market.
To further enhance faculty qualifications and career development, CSU offers faculty development grants, international fellowships, and research mobility programs that allow faculty to engage in cross-disciplinary collaborations with global research institutions. The university also provides internal funding for interdisciplinary research projects that align with regional and national development priorities.
Through these structured mechanisms, CSU ensures that interdisciplinary research is not only encouraged but also formally recognized in faculty tenure, promotion, and research evaluation processes. This comprehensive system reinforces the university’s commitment to fostering multi-disciplinary collaboration, global competitiveness, and impactful scientific contributions to regional and national development.
Caraga State University’s Scopus-Indexed Research Publications Reach an All-Time High
Caraga State University (CSU) continues to expand its research footprint, as evidenced by its all-time publication performance in Scopus. As of the latest data, CSU researchers have collectively contributed 657 scholarly works since 2010, authored by 662 scholars, showcasing the university’s dedication to advancing knowledge across various disciplines.
Based on the latest SciVal data covering the years 2021 to 2025, Caraga State University (CSU) ranks 10th nationwide among Philippine academic institutions in terms of Scopus-indexed scholarly output, with a total of 440 publications produced by 584 researchers. SciVal is an advanced analytics solution, built on a core of Scopus® data, that enables the flexible evaluation of any research field as well as the research performance of individuals, research groups, departments, institutions, and countries.
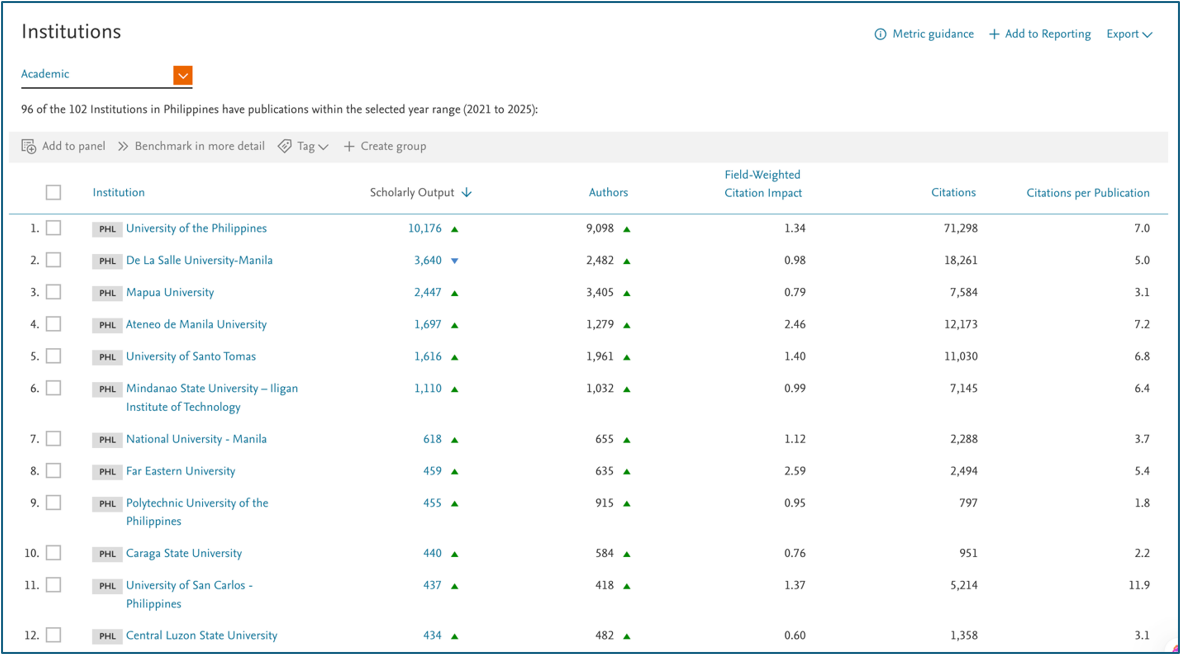
The five-year span (2021–2025) is a critical metric in research analytics as it captures sustained scholarly productivity and impact, allowing for the identification of emerging trends, consistent performers, and areas needing support.
Despite being a relatively young institution in the national research ecosystem, CSU’s performance over this period highlights its accelerating contributions to global scholarship, particularly in multidisciplinary fields, and positions it among the country’s leading academic institutions in research.
In 2024 alone, CSU achieved a remarkable milestone, with 244 research articles accepted and published in Scopus-indexed journals and conference proceedings. While the indexing process takes time, 168 of these publications have already been indexed, further reinforcing CSU’s growing research influence on a global scale. This surge in research output highlights the university’s commitment to fostering a culture of innovation and scholarly excellence.
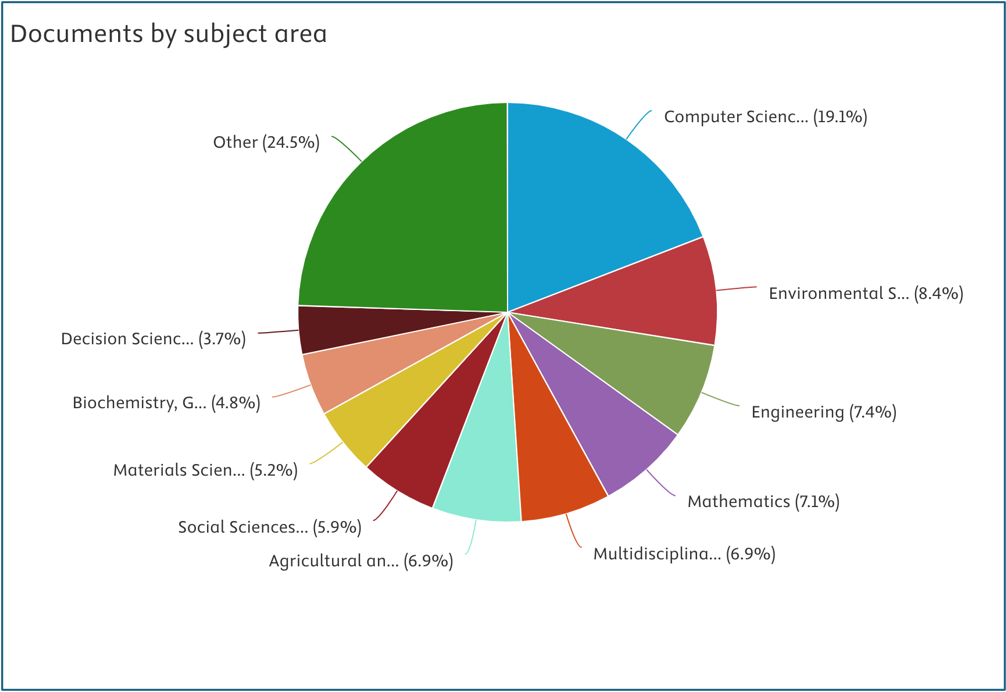
The chart above illustrates the distribution of documents by subject area based on CSU’s Scopus performance report. Key observations include:
- The largest category is “Other” (24.5%), indicating that a substantial portion of research output falls outside the predefined subject classifications.
- Computer Science (19.1%) is the most represented specific discipline, highlighting CSU’s strong research presence in this field.
- Other notable subject areas include:
- Environmental Science (8.4%)
- Engineering (7.4%)
- Mathematics (7.1%)
- Multidisciplinary Research (6.9%)
- Agricultural and Biological Sciences (6.9%)
- Social Sciences (5.9%)
- Materials Science (5.2%)
- Biochemistry, Genetics, and Molecular Biology (4.8%)
- Decision Sciences (3.7%)
This distribution reflects CSU’s diverse research portfolio, with notable strengths in Computer Science, Environmental Science, and Engineering. Meanwhile, Social Sciences and Decision Sciences have a comparatively smaller share, suggesting potential areas for further development.
Productivity and Impact (2021-2025), according to SciVal
| Areas | Scholarly Output | Citations | Authors | Field-Weighted Citation Impact |
| Computer Science | 146 ↓ | 167 | 230 ↑ | 0.51 |
| Multidisciplinary / Intedisciplinary | 84 ↑ | 102 | 190 ↑ | 1.61 |
| Mathematics | 75 ↓ | 75 | 135 ↓ | 0.57 |
| Engineering | 73 ↓ | 196 | 130 ↓ | 0.8 |
| Environmental Science | 72 ↓ | 218 | 121 ↓ | 0.55 |
| Agricultural and Biological Sciences | 63 ↓ | 147 | 107 ↓ | 0.34 |
| Social Sciences | 60 ↑ | 65 | 118 ↑ | 0.46 |
| Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology | 49 ↑ | 56 | 51 ↑ | 0.19 |
| Decision Sciences | 44 ↓ | 43 | 85 ↑ | 0.54 |
| Materials Science | 44 ↑ | 128 | 61 ↑ | 0.55 |
| Chemical Engineering | 41 ↑ | 46 | 41 ↑ | 0.2 |
| Medicine | 38 ↑ | 133 | 81 ↑ | 0.78 |
| Energy | 35 ↓ | 105 | 58 ↓ | 0.81 |
| Chemistry | 33 ↑ | 56 | 23 ↑ | 0.24 |
| Physics and Astronomy | 31 ↓ | 33 | 57 ↓ | 0.85 |
| Earth and Planetary Sciences | 23 ↓ | 69 | 39 ↓ | 0.95 |
| Business, Management and Accounting | 17 ↓ | 73 | 35 ↑ | 0.8 |
| Economics, Econometrics and Finance | 10 ↑ | 30 | 27 ↑ | 1.16 |
| Psychology | 10 ↑ | 26 | 19 ↑ | 0.64 |
| Arts and Humanities | 9 ↑ | 28 | 15 ↑ | 0.84 |
| Immunology and Microbiology | 7 ↑ | 73 | 6 ↑ | 1.89 |
| Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics | 4 ↑ | 20 | 12 ↑ | 0.91 |
| Nursing | 2 ↑ | 8 | 5 ↑ | 1.26 |
The research productivity and impact of Caraga State University (CSU) span multiple disciplines, with varying trends in scholarly output, citations, and author participation. Across all subject areas, from 2021 to 2025, CSU has produced 440 scholarly outputs, receiving 951 citations from 584 authors, with a Field-Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI) of 0.76, indicating a citation rate slightly below the global average.
Growth Areas
Several disciplines have shown an upward trend in research activity and impact. The Multidisciplinary field leads with an FWCI of 1.61, demonstrating a strong research influence relative to global standards. Immunology and Microbiology also stands out with an FWCI of 1.89, despite having only seven scholarly outputs, indicating high citation impact. Economics, Econometrics, and Finance (FWCI: 1.16) and Nursing (FWCI: 1.26) also reflect strong influence despite their smaller scholarly output. Meanwhile, Medicine (38 outputs, 133 citations) and Materials Science (44 outputs, 128 citations) are emerging areas of interest, showing both growth in output and citations.
Declining Fields
Some disciplines have seen a decrease in output and citation performance. Computer Science, despite its 146 scholarly outputs, has an FWCI of 0.51, suggesting that its research impact is below the global average. Similarly, Engineering (FWCI: 0.80), Environmental Science (FWCI: 0.55), and Agricultural and Biological Sciences (FWCI: 0.34) have all experienced declines in scholarly output, citations, and author contributions. Mathematics, with 75 outputs and 75 citations, also saw a decrease in research activity, with an FWCI of 0.57.
Emerging and Niche Fields
Certain subject areas, while having relatively low research output, are showing potential. Arts and Humanities, Psychology, and Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Pharmaceutics all experienced growth in output and citations, signaling increasing research engagement. Earth and Planetary Sciences has a moderate FWCI of 0.95, indicating its citation performance is near the global average.
| Publication Year | Document Title | Authors | Journal | Citations from 2020-2024 (Last 5-Years) | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | A system for monitoring water quality in a large aquatic area using wireless sensor network technology | Demetillo, Alexander T.; Japitana, Michelle V.; Taboada, Evelyn B. | Sustainable Environment Research | 123 | 1 |
| 2020 | Applications of imaging and spectroscopy techniques for non-destructive quality evaluation of potatoes and sweet potatoes: A review | Sanchez, Philip Donald C.; Hashim, Norhashila; Shamsudin, Rosnah; Mohd Nor, Mohd Zuhair | Trends in Food Science and Technology | 88 | 2 |
| 2016 | Vertical accuracy assessment of 30-M resolution ALOS, ASTER, and SRTM global DEMS over Northeastern Mindanao, Philippines | Santillan J.R.; Makinano-Santillan M. | International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences - ISPRS Archives | 86 | 3 |
| 2020 | Accounting for symptomatic and asymptomatic in a SEIR-type model of COVID-19 | Arcede, Jayrold P.; Caga-Anan, Randy L.; Mentuda, Cheryl Q.; Mammeri, Youcef | Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena | 43 | 4 |
| 2017 | Development of gallic acid-modified hydrogels using interpenetrating chitosan network and evaluation of their antioxidant activity | Kang, Byungman; Vales, Temmy Pegarro; Cho, Byoung-Ki; Kim, Jong-Ki; Kim, Ho-Joong | Molecules | 41 | 5 |
| 2021 | Cloud Computing Adoption Intention by MSMEs in the Philippines | Matias, Junrie B.; Hernandez, Alexander A. | Global Business Review | 35 | 6 |
| 2023 | In-depth study of tomato and weed viromes reveals undiscovered plant virus diversity in an agroecosystem | Rivarez, Mark Paul Selda, et al. | Microbiome | 33 | 7 |
| 2022 | Emerging nondestructive techniques for the quality and safety evaluation of pork and beef: Recent advances, challenges, and future perspectives | Sanchez, Philip Donald C., et al. | Applied Food Research | 31 | 8 |
| 2018 | Tools for circular economy: Review and some potential applications for the Philippine textile industry | Balanay, Raquel; Halog, Anthony | Circular Economy in Textiles and Apparel: Processing, Manufacturing, and Design | 31 | 8 |
| 2021 | Circular Economy across Australia: Taking Stock of Progress and Lessons | Anthony Halog, Raquel Balanay, Sandra Anieke & Tsz Yan Yu | Circular Economy and Sustainability | 30 | 9 |
| 2018 | Glycoproteomic Alterations in Drug-Resistant Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Cells Revealed by Lectin Magnetic Nanoprobe-Based Mass Spectrometry | Juanilita T. Waniwan; Yi-Ju Chen; Rey Capangpangan; Shao-Hsing Weng; Yu-Ju Chen | Journal of Proteome Research | 30 | 9 |
| 2021 | Impact of vaccine supplies and delays on optimal control of the COVID-19 pandemic: mapping interventions for the Philippines | Carlo Delfin S. Estadilla, Joshua Uyheng, Elvira P. de Lara-Tuprio, Timothy Robin Teng, Jay Michael R. Macalalag, Maria Regina | Infectious Diseases of Poverty | 25 | 10 |
| 2020 | Development of poly (2-Methacryloyloxyethyl Phosphorylcholine)-functionalized hydrogels for reducing protein and bacterial adsorption | Temmy Pegarro Vales; Jun-Pil Jee; Won Young Lee; Sung Cho; Gye Myung Lee; Ho-Joong Kim; Jung Suk Kim | Materials | 25 | 10 |
Notable Trends in Research Output
- COVID-19-related research has also gained significant attention, such as:
o SEIR-type modeling for symptomatic and asymptomatic COVID-19 cases (43 citations)
o Impact of vaccine supplies and delays on pandemic control in the Philippines (25 citations) - Emerging research areas include Circular Economy, Cloud Computing Adoption, Viromes in Agroecosystems, and Nondestructive Food Quality Evaluation with growing citation counts.
Key Observations on Citation Impact
- The highest-ranked paper (2019) has 123 citations, reflecting strong engagement in environmental and sensor-based research.
- Papers from 2020-2021 show substantial citations, indicating their relevance and impact in the last five years.
- Multidisciplinary research areas such as food science, materials science, environmental monitoring, and mathematical modeling are gaining traction.
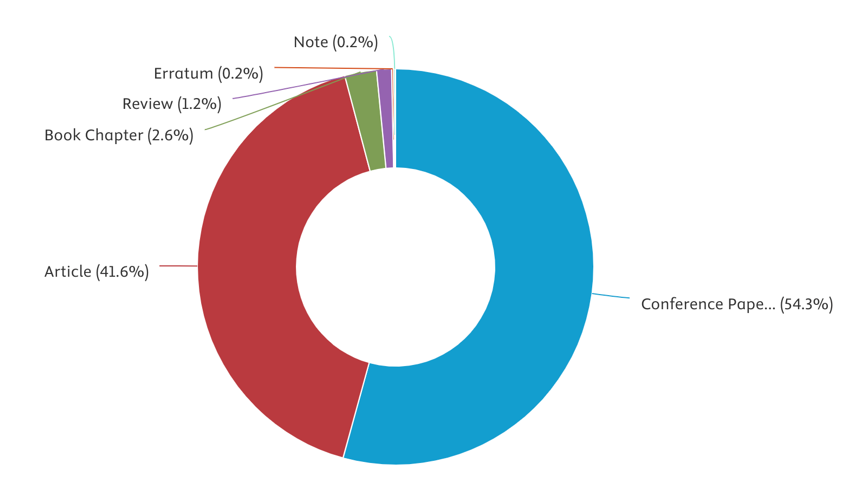
The chart provides an overview of the distribution of research output by document type based on CSU’s Scopus performance report. This breakdown highlights the preferred avenues for academic dissemination among CSU researchers.
Key Takeaways:
- Conference Papers (54.3%) represent the largest share, indicating that a significant portion of research findings is presented at conferences rather than published in journals.
- Journal Articles (41.6%) make up a substantial portion, showcasing CSU’s strong engagement in peer-reviewed scholarly publishing.
- Other document types contribute to a smaller share of total research output, including:
- Book Chapters (2.6%)
- Reviews (1.2%)
- Errata (0.2%)
- Notes (0.2%)
This distribution suggests that CSU researchers heavily rely on conference proceedings for academic dissemination, which facilitates rapid knowledge sharing and networking opportunities. However, increasing the proportion of journal articles may enhance the citation impact and long-term visibility of research output.
Below are the top contributors per area (Source: Scopus):
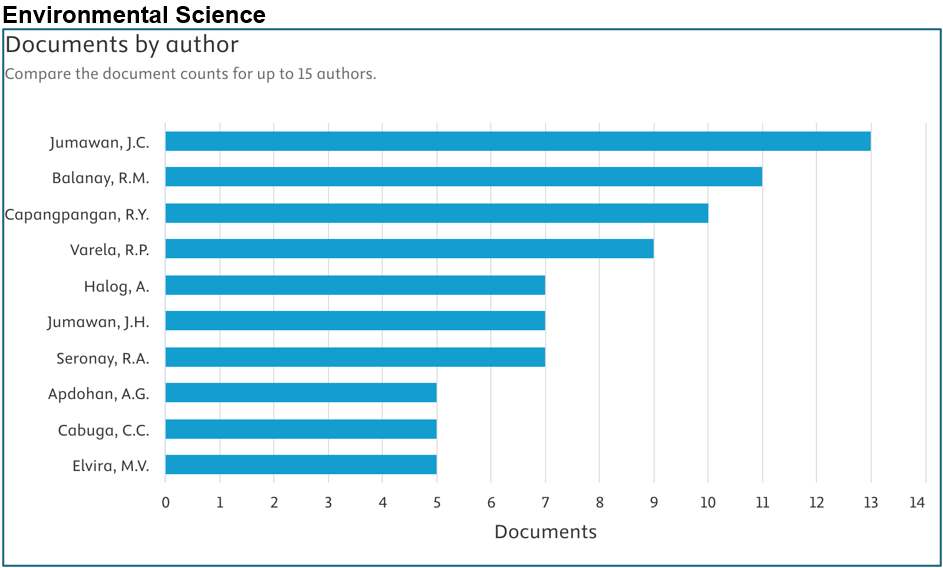
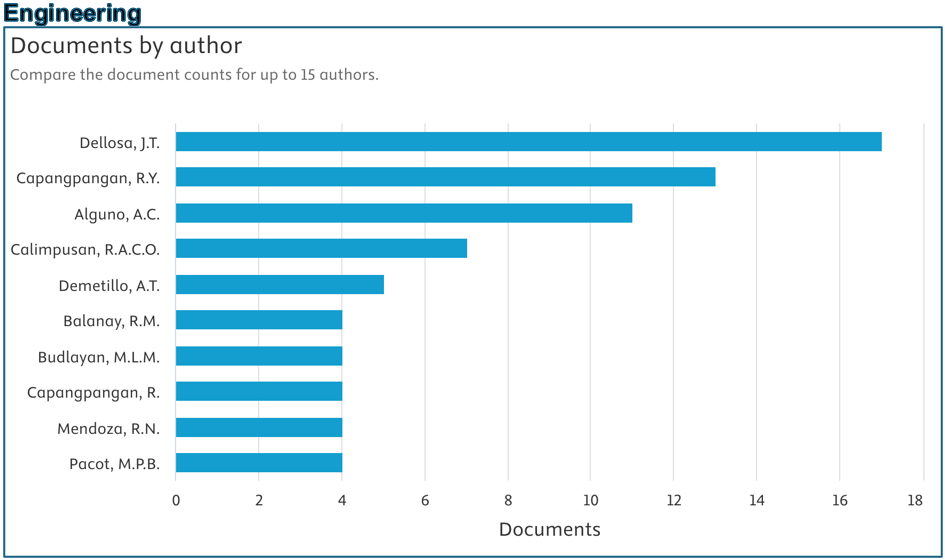
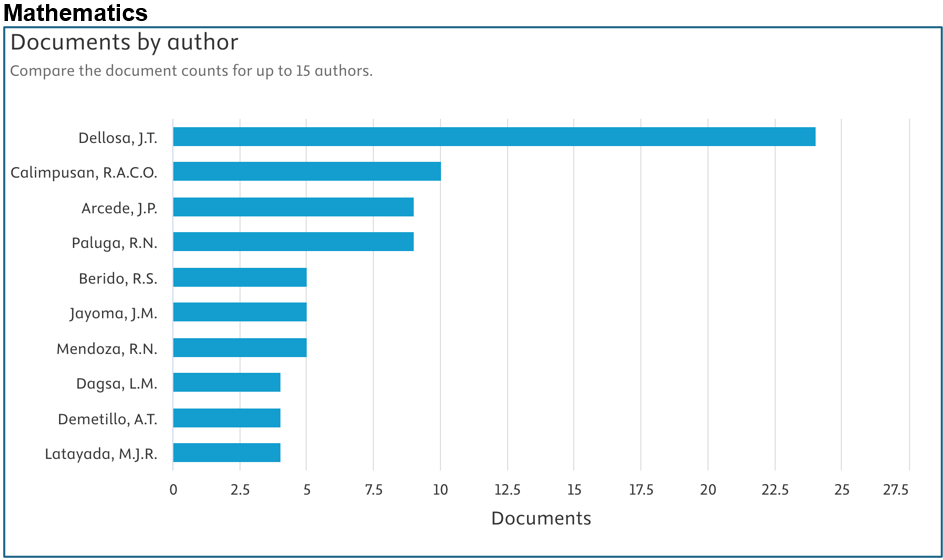
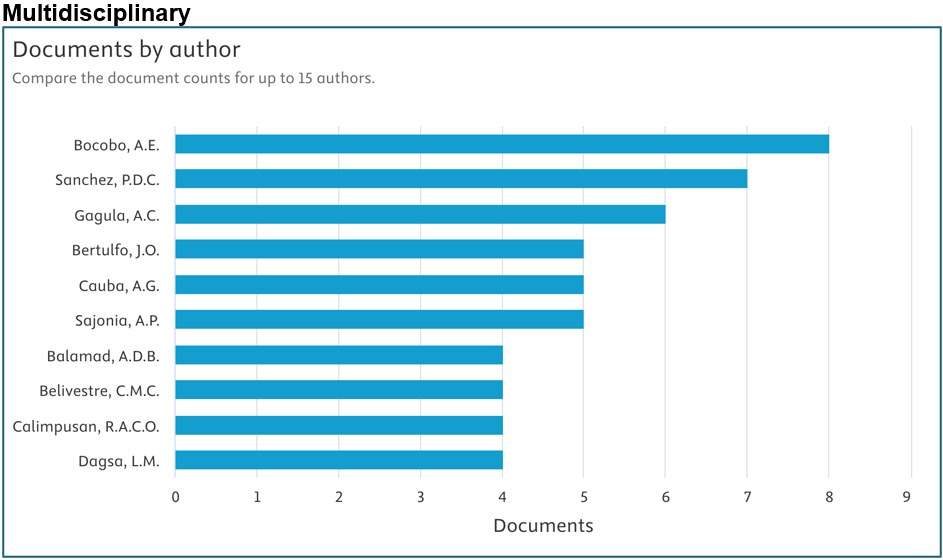
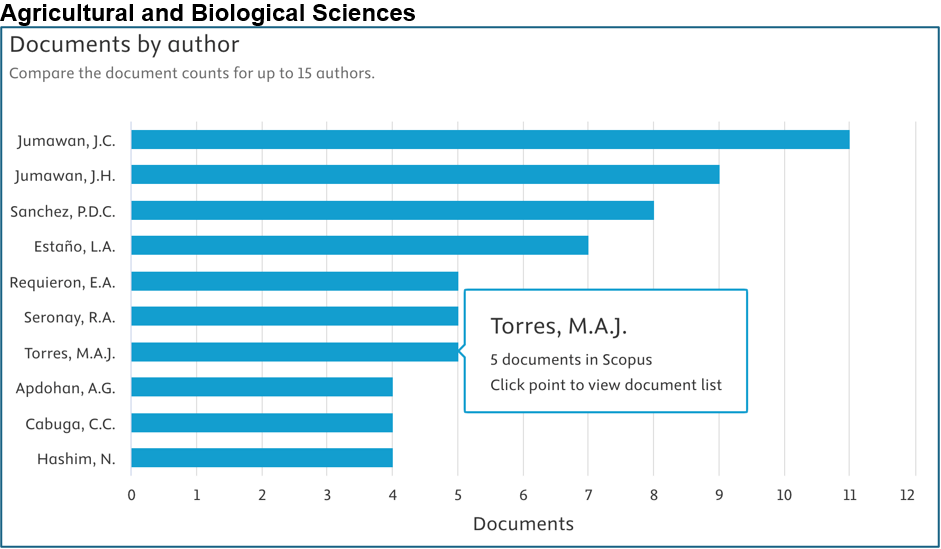
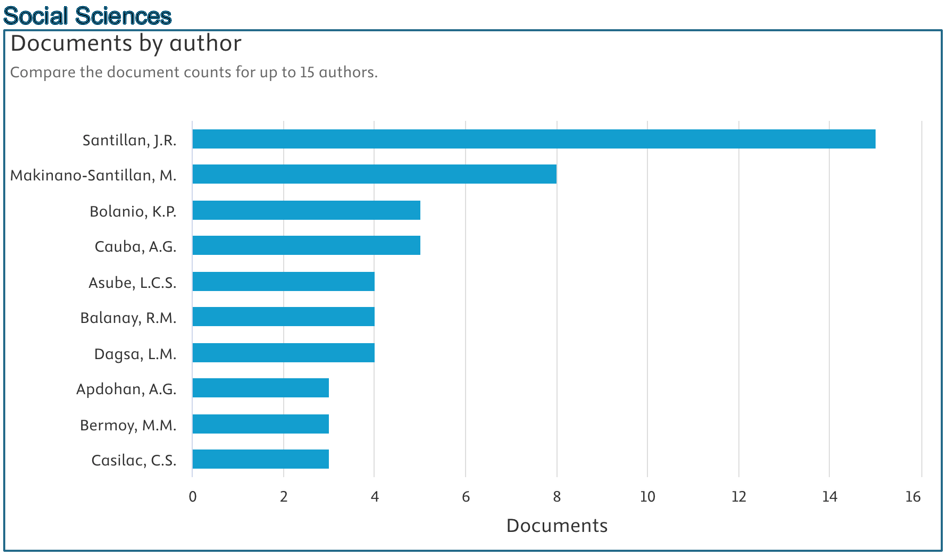
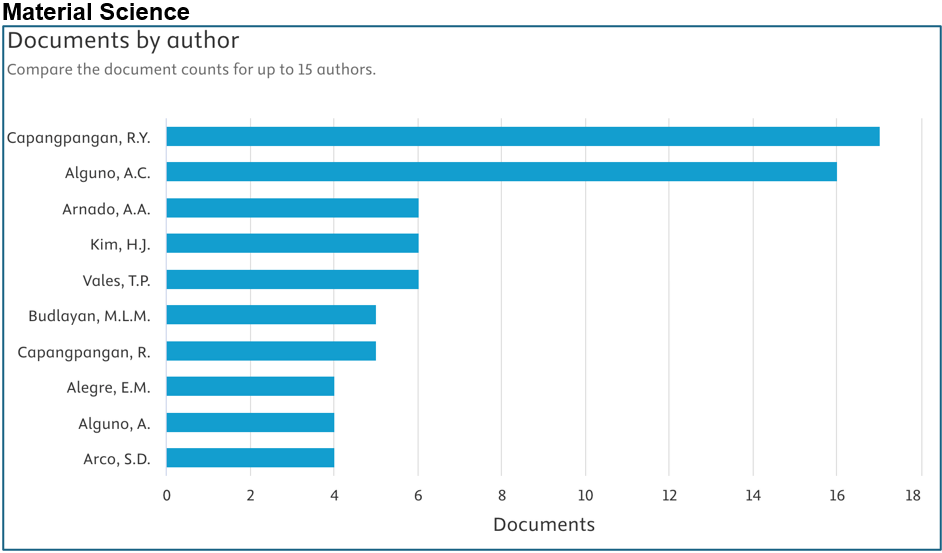
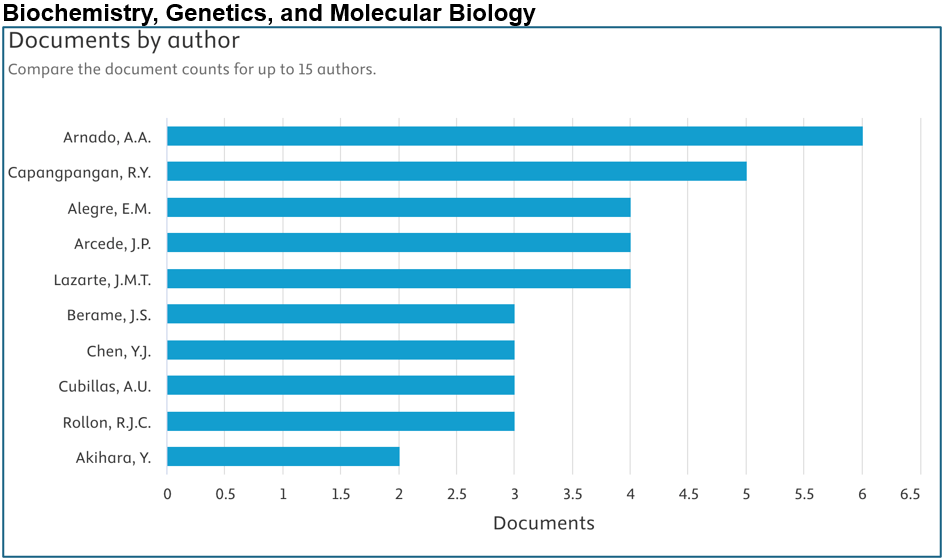
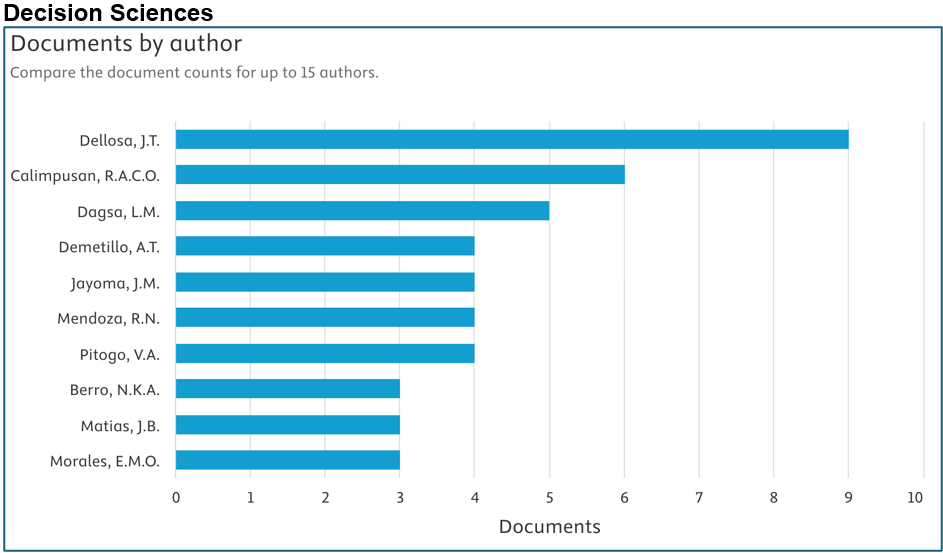
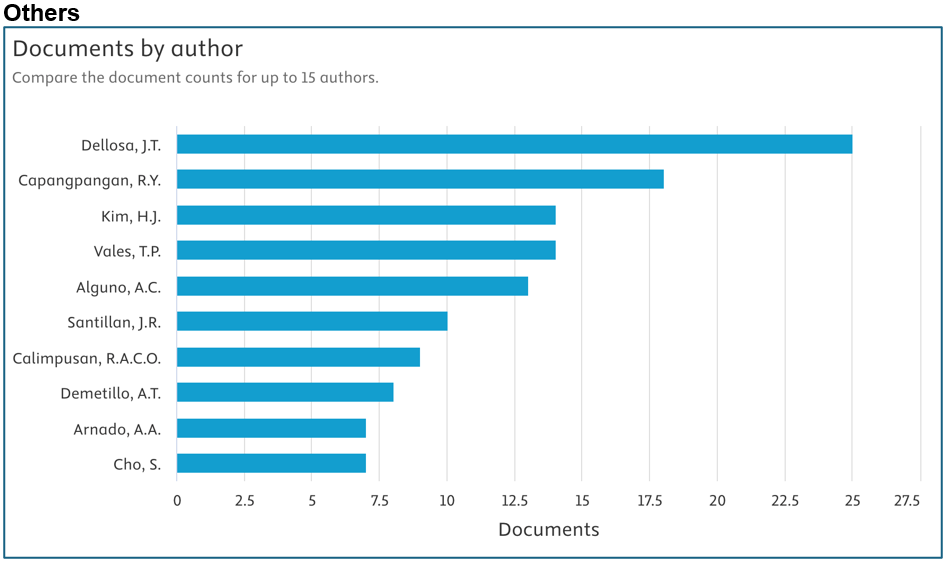
Prepared by: Dr. Junrie B. Matias, RDIE Publication Management Office Director
CSU Interdisciplinary Research Projects in 2023
| R&D Projects | Funding Agency | PROJECT LEADER | Research Workers | Disciplines Interdisciplinary Research | Project Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Development of Paper-based Colorimetric Sensor Utilizing Varied Sizes of Gold Nanoparticles for Rapid and On-site Detection of Various Meat Products Spoilage | CHED | Dr. Felmer Latayada | Jeanne Phyre Lagare-Oracion, Jamiela Sakuddin |
Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics | 11,717,724.00 |
| Needs Assessment of HEIs in BARMM towards Enhancing Their Research Competencies through an Institutional-Level Sustainable Professional Development Model | CHED-HECBOL | Dr. Rowena P. Varela | Rowena P. Varela, Rey Y. Capangpangan, Joycelyn C. Jumawan, Romell A. Seronay, Meriam M. Santillan, Jojene R. Santillan, Raquel M. Balanay, Miraluna L. Herrera, Jayrold P. Arcede, Anthony M. Penaso |
Agriculture, Mathematics, Chemistry, Geodetic Engineering, Biology | 10,000,000.00 |
| SuMMO Industry 4.0 Project 1: ICT4RM2.0 | DOST (S4CP) | Rolyn C. Daguil | Alexander T. Demetillo, Michelle Japitana |
Information Technology, Computer Science, Electronics Egnineering, Geodetic | 11,559,330.36 |
| SuMMO Industry 4.0 Project 2: Mine GEARS | DOST (S4CP) | Rudolph Joshua U. Candare | Michelle V. Japitana, Ydron Paul C. Amarga, Ronnel O. Cacho, Christopher Arizala, Adrian Pete R. Lagare, Sheenave A. Falcon |
Information Technology, Computer Science, Electronics Egnineering, Geodetic | 6,987,724.72 |
| SuMMO Industry 4.0 Project 3: MARVEL Technologies | DOST (S4CP) | Jaymer M. Jayoma | Engr. Gerome L. Amper Engr. Adrian L. Melana, Elbert S. Moyon, Edsel Matt O. Morales, Kent T. Espejon, Eunessa Mae T. Alob, Jayson C. Dollete, Kier Patrick A. Empang, Clifford T. Eco, Arnel A. Rosillo |
Mining, Electronics, Environmental Science, Information Technology, Computer Science | 11,141,364.05 |
| Artificial Intelligence Program: Design and Development of an Intelligent Traffic Control and Management System | DOST-PCIEERD | JUNRIE B. MATIAS | Dr. Junrie B. Matias, Engr. Rudolph Joshua Candare, El Bajadour Villacampa, Re-ann Cristine Calimpusan |
Information Technology, Computer Science, Electronics Egnineering, | 4,977,500.00 |
| Well-Being, Realizations, and Aspirations of the Indigenous People's Students from Poverty-Stricken Families in Caraga Region | DOST XI -NRCP | Dr. Trixie E. Cubillas | Education, Social Science, Social Work | 900,000.00 | |
| Virtual Workspace During Covid-19 Pandemic: Changing Landscapes in Work Dynamics of Academics in Caraga Region | DOST-NRCP-NSTEP | Jan Rey Flores | Connie Fern Miranda, Rex Makinano, John Albert Quijano |
Education, Social Science, Social Work | 1,000,000.00 |
| Lumad Spirituality in the Time of COVID-19 Pandemic | DOST-NRCP-NSTEP | Ana Maria Belinda yting | Jan Rey Flores, Cedrix Von Alesna |
Biology, Social Science, Social Work | 900,000.00 |
| Assessment of Plastic Debris and Microplastics in Different Specimen (Fish, Sediment, Water, Benthic organisms) in Selected Aquatic Environments in Mindanao and Exploration of Relative Stress Biomarkers | DOST-NRCP | Dr. Rey Capangpangan | Dr. Romell Seronay, Dr. Joycelyn Jumawan, |
Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics, Environmental Science | 6,242,997.20 |
| Upgrading of dairy carabao facility in support to research and development in Caraga Region | ACEF EXECOm thru DA | Dr. Tomas Austral | Agriculture, Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering | 5,000,000.00 | |
| Biodiversity Assessment and Monitoring System for Tinuy-an Falls Protected Landscape | DENR-PENRO Surigao del Sur | Romell A. Seronay | Environmental Science, Biology, Agricultur | 750,000.00 | |
| Research-Based Establishment of Sustainable and Integrative Learning Innovations, Engagement and Nurturing Techniques (RESILIENT) Program Towards Immersive Flexible Education | CHED | Dr. Luisito I. Tabada | Mrs. Ruth E. Sanchez | Psychology | 1,057,012.00 |
| Dr. Miraluna L. Herrera | Mathematics | ||||
| Dr. Gladys L. Lagura | Education | ||||
| Engr. Michelle V. Japitana | Geodetic | ||||
| Dr. Rowena P. Varela | Agriculture | ||||
| Dr. Armie Leila M. Mordeno | Adminstration and Finance | ||||
| Facile Synthesis of Smart Thermo-responsive Sago Starch/Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels Crosslinked with Methacrylated-TiO2 for Heavy Metal Valorization and Photocatalysis | PCIEERD Balik Saliksik Grant | Dr. Temmy P. Vales | Chemistry, Bioology, Physics, Social Science | 1,270,600.00 | |
| Selective Electrochemical Detection of Mercury ions using PEDOT-wires functionalized silica nanochannel | PCIEERD Balik Saliksik Grant | Dr. Deomila Basnig | Chemistry, Bioology, Physics, Social Science | 1,995,984.00 | |
| Biochartilant Project (Phase 3): Multi-location Trials | DA-BAR | Reuben James Rollon | Agriculture, Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology | 4,280,747.24 | |
| Towards Management of Abaca Virus Diseases Using Sensitive Tools: Updating Nature of Diseases and Incidence. | DA-Biotech | Dr. Elizabeth Parac | Agriculture, Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology | 2,897,816.22 | |
| Socio-Economic Benefits of Calibunan Fish Sanctuary to the coastal communities of Cabadbaran City | LGU-Cabadbaran City | Dr. Romell A. Seronay | Agriculture, Environmental Science, Social Sciences | 150,000.00 | |
| Solid Waste Characterization, Management Practices and Suitability Mapping for Sanitary Landfill in Bongao, Tawi-Tawi | CHED-HECBOL | Dr. Romell A. Seronay | Agriculture, Environmental Science, Social Sciences | 200,000 | |
| Regional Intellectual Property and Technology Business Management (IPTBM) in Caraga through the RAISE Program | DOST PCAARRD | Kenneth L. Ciudad | Agriculture, Information Technology, Engineering, Computing, Environmental Science | 3,983,650.00 | |
| Establishment of Regional Agri-Business Hub (ABH) in Caraga through the RAISE Program | DOST PCAARRD | Genesis Jared A. Cutamora | Agriculture, Information Technology, Engineering, Computing, Environmental Science | 2,278,800.00 | |
| Establishment of a Regional Agri-Aqua Technology Business Incubator (ATBI) in Caraga through the RAISE Program | DOST PCAARRD | Melbert R. Bonotan | Agriculture, Information Technology, Computing, Environmental Science | 5,251,309.99 | |
| Establishment of a Regional Knowledge Management hub in Caraga through the RAISE Program | DOST PCAARRD | Meycel C. Amarille | Agriculture, Chemistry, Physics, Engineering | 2,279,000.00 | |
| Biological Profiling of Can-agtiw Watershed in Malimono, Agas-agas Watershed in Taganaan and Baoy Watershed in Claver and Gigaguit, Surigao del Norte | SEDMFI / USAID | Romell A. Seronay | Environmental Science, Biology, Agriculture, Social Sciences | 1,500,000.00 | |
| DA-BIOTECH-R2306: Towards Management of Abaca Virus Disease Using Sensitive Tools: Updating Nature of Diseases and Incidence | DA-BAR | Elizabeth P. Parac | Agriculture, Mathematics, Chemistry, Biology | 2,897,816.22 | |
| Optimization of sea water using magnesium chloride (mgcl2) as a moisture binder for dust suppressant in nickel mining operations | Coral Bay Nickel Inc | Engr. George Dotdot Mystic P. Banias Charles Wyndel S. Cleofas Joselito R. Asenerio |
Engineering, Chemistry | 115,000.00 | |
| 101,334,376.00 |

